ABSTRACT DATA STRUCTURES STACK AND QUEUE

Describe the characteristics and applications of a stack
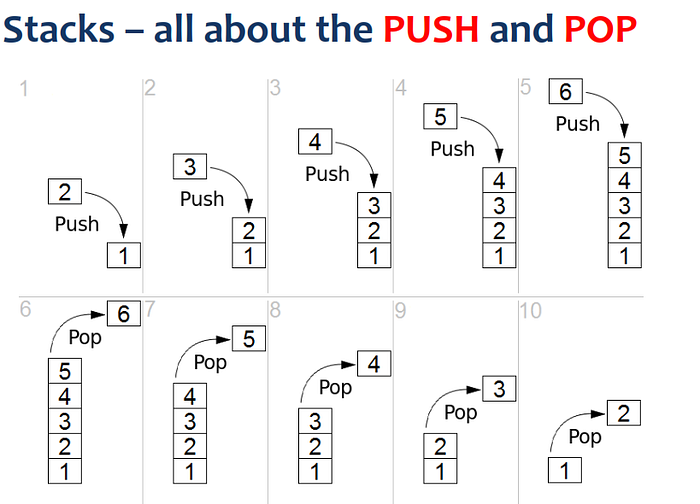
A stack is a data structure that follows the Last In, First Out (LIFO) principle, where the last element added to the stack is the first one to be removed.

package practice;
import java.util.Stack;
public class one {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Stack<Integer> a=new Stack<Integer>();
a.add(10);
a.add(20);
a.add(30);
a.add(40);
System.out.println("Size"+" "+a.size());
display(a);
System.out.println("pop ="+a.pop());
System.out.println("peek ="+a.peek());
System.out.println("isempty ="+a.isEmpty());
}
private static void display(Stack<Integer> a) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for (int i =a.size()-1; i >=0; i--) {
System.out.println(a.get(i));
}
}
}Output:
Size 4
40
30
20
10
pop =40
peek =30
isempty =falseExplanation:
- Creating a Stack: We create a
Stackinstance to holdIntegervalues. - Pushing Elements: We use the
push()method to add elements to the stack. The stack after pushing four elements [10, 20, 30,40] is printed. - Popping an Element: The
pop()method removes and returns the top element of the stack. The element is printed. - Peeking the Top Element: The
peek()method returns the top element without removing it from the stack. - Checking if the Stack is Empty: The
isEmpty()method checks whether the stack is empty. - Getting the Size of the Stack: The
size()method returns the number of elements in the stack.
Describe the characteristics and applications of a queue
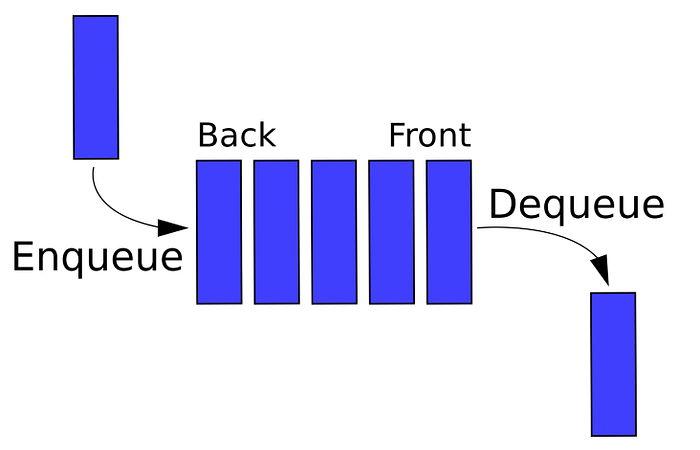
A queue is a data structure that follows the First In, First Out (FIFO) principle, where the first element added to the queue is the first one to be removed. The Queue interface is part of the java.util package, and it can be implemented using various classes like LinkedList, PriorityQueue, etc.
package practice;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class one {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Queue<Integer> q=new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(10);
q.add(20);
q.add(30);
q.add(40);
System.out.println("size ="+q.size());
display(q);
System.out.println("remove ="+q.remove());
System.out.println("peek ="+q.peek());
System.out.println("is empty ="+q.isEmpty());
}
private static void display(Queue<Integer> q) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for (Integer integer : q) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
}
}Output:
Size 4
10
20
30
40
remove =10
peek =20
is empty =falseExplanation:
- Creating a Queue: We create a
Queueinstance to holdIntegervalues using theLinkedListclass. - Adding Elements: We use the
add()method to add elements to the queue. The queue after adding four elements [10, 20, 30,40] is printed. - Removing an Element: The
remove()method removes and returns the front element of the queue. - Peeking the Front Element: The
peek()method returns the front element without removing it from the queue. - Checking if the Queue is Empty: The
isEmpty()method checks whether the queue is empty. - Getting the Size of the Queue: The
size()method returns the number of elements in the queue.
Happy coding!